Sub-Theme
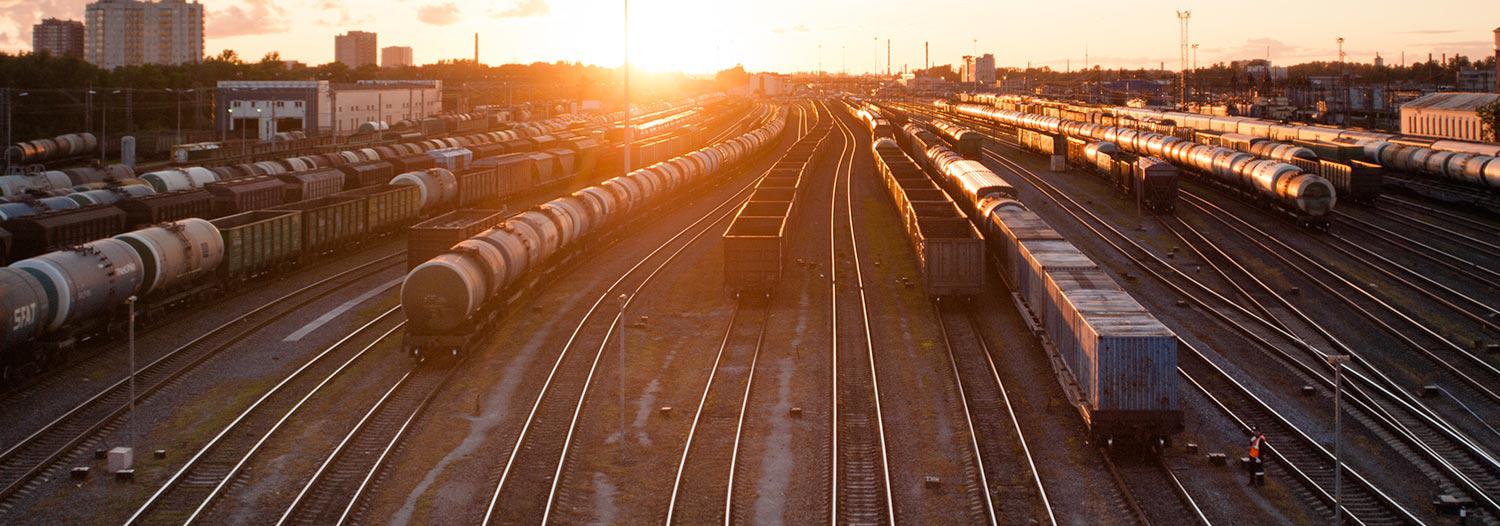
Roads
Roads are defined paths for the transfer of goods or movement of vehicles, people or animals. Unlike Railways, Roads do not have fixed tracks. The Roads dataset includes cycleways, foot tracks and ferry routes.
National Datasets in this Sub-Theme
Purpose
The Road dataset is an aggregation of data from multiple jurisdiction sources which depicts national and accurate road based information.
Classification depending upon its purpose or importance, such as a national highway that connects capital cities, arterial roads which connect major regional centres or move large volumes of traffic across metropolitan areas, down to access roads which provide access to buildings within properties centrelines.
Dataset Uses
- Routeing, traffic flow management and economic analysis
- the development of routeing road networks for use by freight and logistics companies, emergency service / response authorities, and general public includes: shortest distance, fastest time and presence/absence of obstacles or restrictions depending upon mode of transport - name, structure, weight/height/speed limits or some other weighting
- fuel-efficient fleet management and self-drive vehicles - require full transport surface specifications including slope, camber, etc.
- predicting, analysing and modelling passenger and freight vehicle movements, and accidents, when joined with business or statistical information for analysis. May only need a list by name, but possibly also location and intersection with other roads, railways, crossings etc.
- Context for other location information
- context for other features over local or small project areas - may show location, name, surface and user access
- context for other features on topographic maps, or other regional or national tourist maps - usually name, class, surface, and route number, obstacles or barriers
- context for charts and reference maps - generally only the location of higher order roads shown
- Asset management, infrastructure protection and public safety
- asset management systems by roads authorities
- identification of infrastructure vulnerable to different hazards
- Service provision
- Being able to calculate the remoteness of communities by comparing a location to the nearest urban centres, particularly to identify areas poorly served by medical facilities
- funding determinations for infrastructure investment
- Analysis of other foundation datasets to determine
- unique addresses within a locality and its neighbours
- the location (as a boundary or an important artery) of administrative boundaries such as local government areas, localities and statistical geographies
Standards and Specifications
Access and Licensing
Access and Licensing Details
Quality
- The roads component of this dataset conforms to the Intergovernmental Committee on Surveying & Mapping's roads data model and PSMA's business rules for this product
- Accuracy of data varies from:
- Approximately 2m in metropolitan areas
- 10–20m in urban fringe and rural areas
- 50–150m in remote areas. There are breaks in connectivity at state borders
Data is six months old when released to market but in rural and remote areas features have a currency of 5–20 years
- Information is available that describes:
- Type of road
- Surface
- User access and physical restrictions
This information is at various levels of completeness depending upon the jurisdiction. Information may also not be consistently classified between states and territories – for example, an arterial road in one state may not be the same as an arterial road in another
- The product is GIS-ready in a range of formats depending upon the distributor
Current Status
In each jurisdiction, the land management or mapping agency creates and manages datasets representing the location of a road, which may be integrated from data held by transport authorities, or derived from GPS data, roads defined in the cadastre, or from interpretation from satellite- or airborne imagery. New roads derived from subdivisions are included in state and territory datasets within two weeks of being lodged.
Until 2006, data captured under Commonwealth mapping programs was not integrated with state and territory datasets. Since 2006, data captured in collaboration with the Commonwealth under the National Topographic Information Coordination Initiative will also be incorporated into state/territory datasets – these are mostly roads in rural and remote areas which have not been revised for up to twenty years. As these are significant updates to a large number of roads over large areas, it will take some time to be integrated into state and territory roads datasets.
Roads datasets are released as products by the states and territories, or supplied to PSMA Australia Pty Ltd (PSMA) for aggregation into a national information product and distributed through a value-added reseller network.
States and territories have legislative responsibilities under various roads management acts for specifically gazetted roads. Local government and private entities manage the remaining road network.
The Commonwealth provides funding for roads maintenance, safety and development under various infrastructure investment and road safety programs. The Commonwealth in particular prioritises funding for the National Network, which comprises roads and other transport infrastructure deemed as nationally significant.
The private sector (e.g. Nokia, Sensis and Intelematics) also manages significant roads datasets particularly as an input to in-car navigation systems. These companies may utilise existing government information as a basis for their datasets, or capture and maintain their own datasets.
There is currently no single vertical integration of roads datasets, as listed, for the national coverage.
Future Status
Short-term objectives
Provide a nationally consistent roads dataset which supports and delivers roads information through the vertical and horizontal integration of the listed datasets. This will allow linking of the location of these features across all themes.
Dataset custodianship will sit with the relevant state and territory land management authority.
An national custodianship of the national roads dataset needs to be identified. Significant stakeholders include:
- Department of Infrastructure and Regional Development, as the lead Australian Government agency on transport and regional affairs
- Bureau of Meteorology, as the lead agency under the Commonwealth Water Act 2007 for water flow modelling and forecasting
- Commonwealth Grants Commission, due to its role in assigning funding to state governments through GST revenue
- Geoscience Australia, due to its role as the national mapping authority and its close collaboration with state and territory agencies in maintaining all topographic information, its role in maintaining information on exposure of infrastructure to hazards, and its underpinning role in providing spatial advice to other parts of Australian Government.
- Austroads , as the representative agency of road transport and traffic authorities in Australia (and New Zealand)
The National Topographic Information Coordination Initiative will continue to address consistency issues in dataset content, and compliance with the ICSM Roads Data Model, by:
- integrating the GEODATA Topo-250K data content into datasets managed by the states and territories, with subsequent aggregation by PSMA
- undertaking data capture programs to bring state and territory information up to the ICSM Roads Data Model content specifications
- national information products will be made available as web services
Medium-term objectives
- Roads information included in national topographic mapping products will be derived from the datasets in the states and territories
- Data held by transport authorities, which is categorised as part of the foundation, will be integrated with the foundation datasets
- Agreement reached with private providers of roads information on inclusion of highly positional accurate roads into authoritative datasets, and agreement on constitution of foundation roads datasets
- Roads will be captured no greater than 1m in urban areas and between 2m and 10m in remote areas if captured from imagery
Long-term objectives
- National information products will have near-real-time currency – roads recently gazetted will be made available in the national product overnight
- All national information products will be available under open access arrangements (for example, by CC-BY) at zero cost
- Review of constitution of foundation roads datasets due to changes in operating environments